Ruminants
•
Dec 12, 2025
•
4 min read
Bypass fats in ruminants: NEB, digestion and technical solutions
Why fats matter in dairy cows, how they help offset Negative Energy Balance (NEB), and which bypass solutions (calcium soaps, fractionated and hydrogenated fats, MCFAs and omega profiles) Nutrion offers.

What are fats
- Fats are molecules insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents.
- Essential component in the diet of ruminants, regardless of the dominant feeding regime.
- 90% of lipids are triglycerides
- 10%: monoglycerides, diglycerides, free fatty acids, sterols, phospholipids, glycolipids, vitamins, pigments.
Functions
- Structural components of cell membranes.
- Energy reserve.
- Thermal insulation.
- Energy supply.
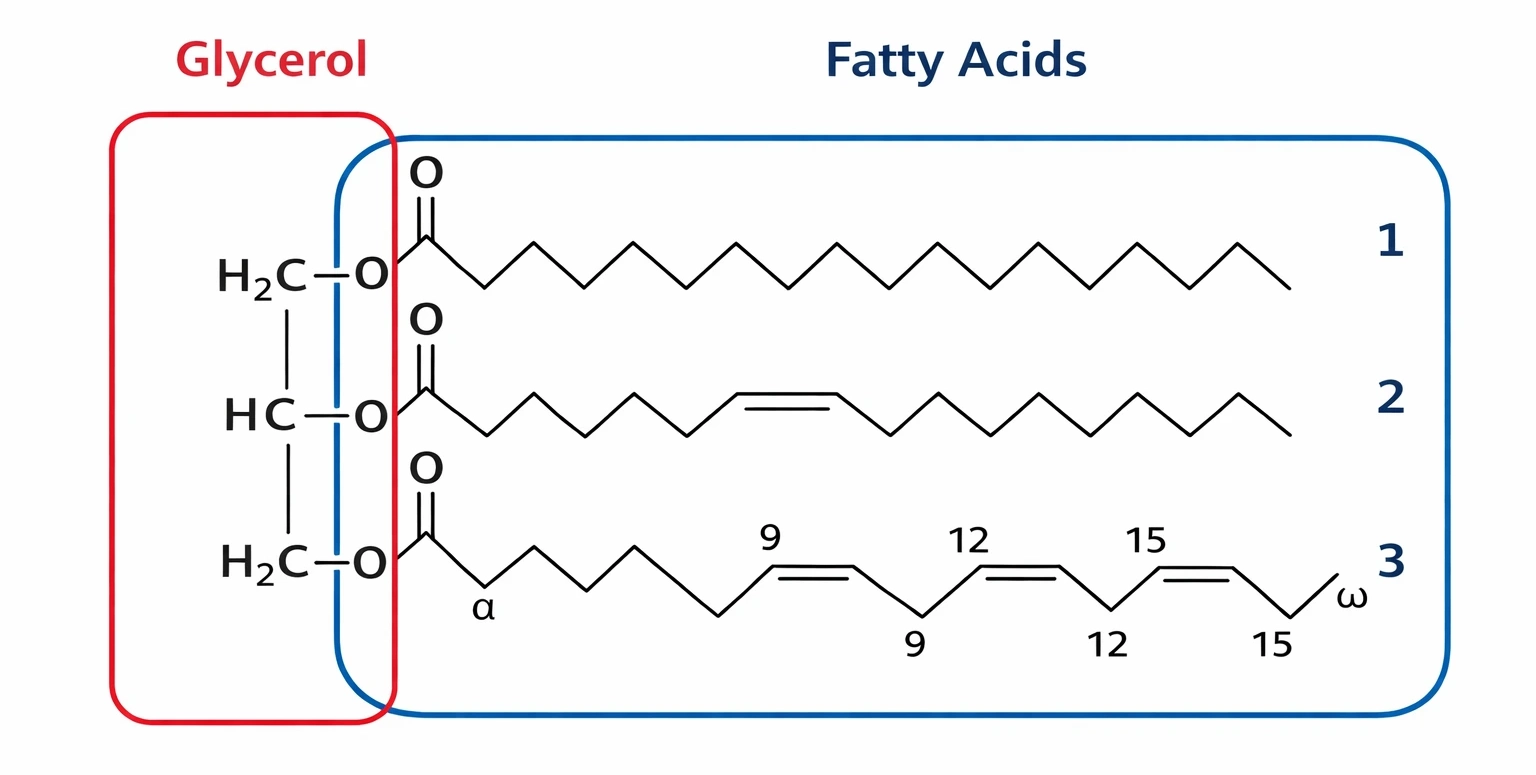
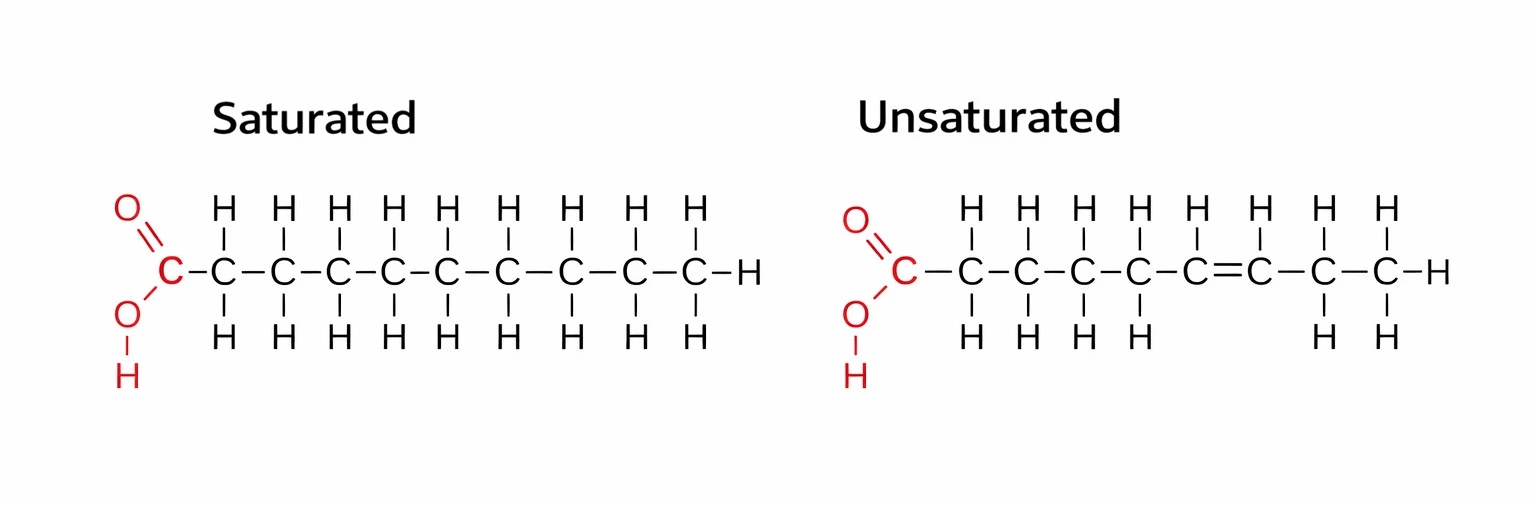
What are fatty acids?
Molecules composed of hydrocarbon chains ending with carboxylic acid groups.
Animal Nutrition
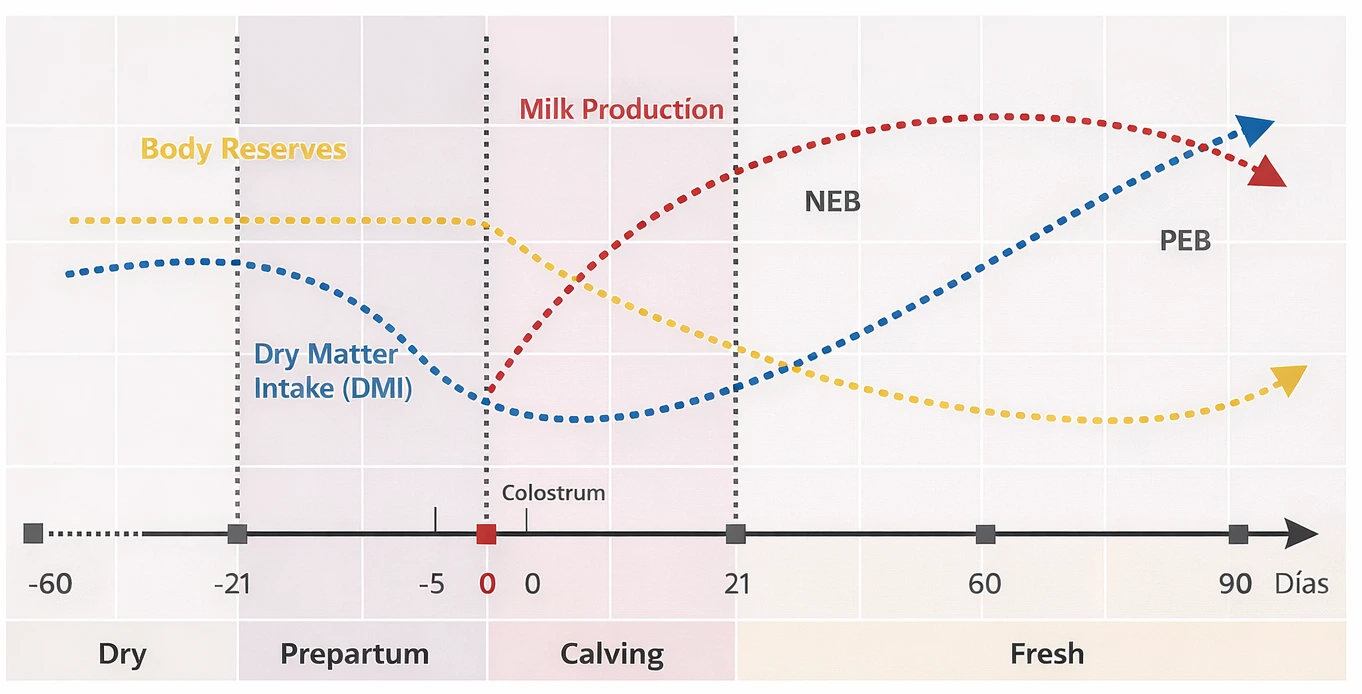
Fats play a fundamental role mainly in dairy cow nutrition.
The most critical period for dairy cattle is at the beginning of lactation, as during this period there is a difference between the amount of energy consumed and the amount required by the animal.
What does this mean?
That the cow is not able to cover her nutritional needs when she needs it most, which causes the mobilization of her body reserves.
Negative effects
- Loss of body condition.
- Affects production.
- Affects reproductive function.
How to counteract NEB?
Increase the energy of the diet
How to do it without affecting ruminal fermentation?
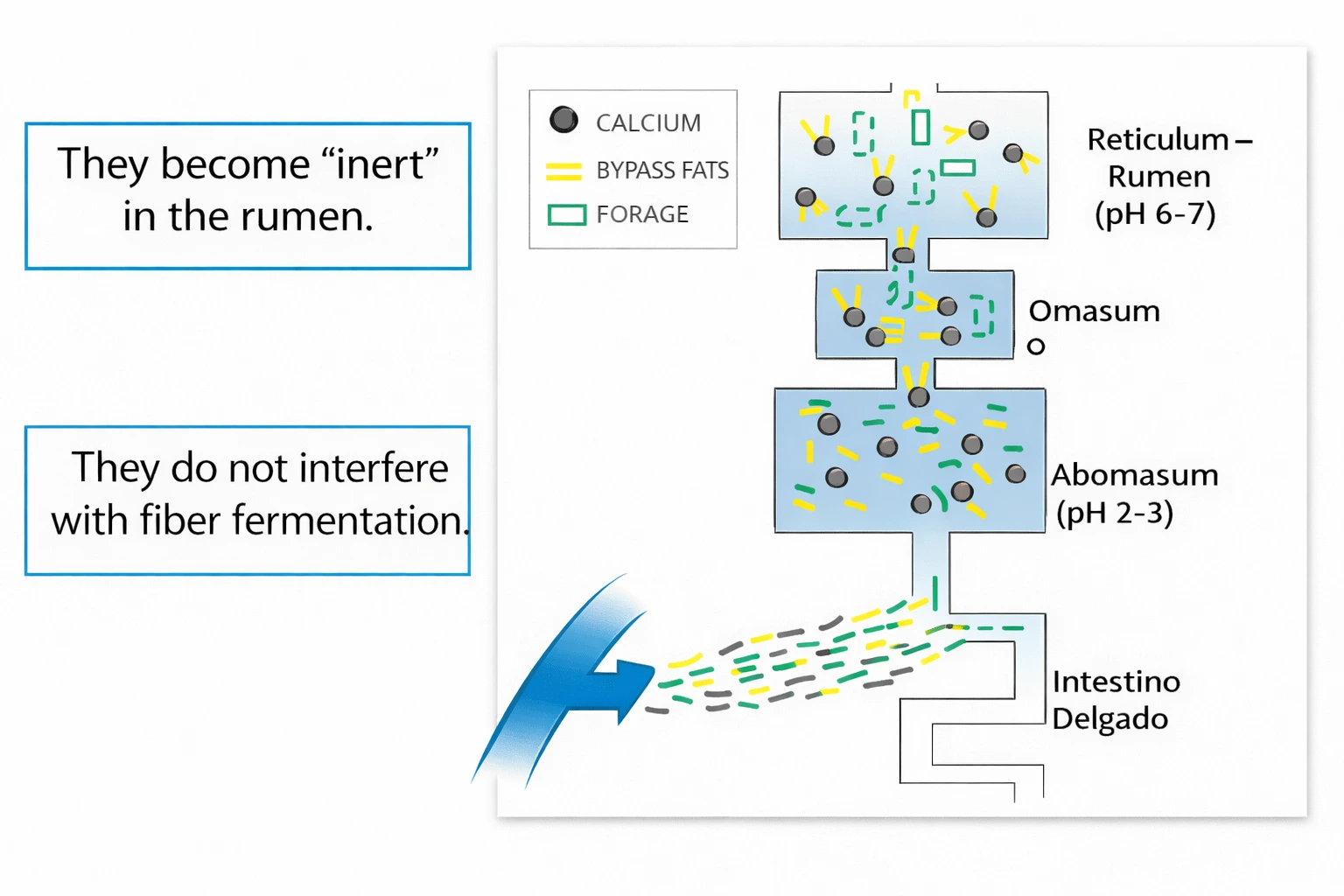
By using Protected Fats (By-Pass)
They pass through the rumen without interfering with its function and are digested in the small intestine.
- They become "inert" in the rumen.
- They do not interfere with fiber fermentation.
Energy comparison
| Nutrient | Energy |
|---|---|
| Proteins | 4 Kcal/gr |
| Carbohydrates | 4 Kcal/gr |
| Fats | 9 Kcal/gr |
They provide 2.5 times more energy than carbohydrates.
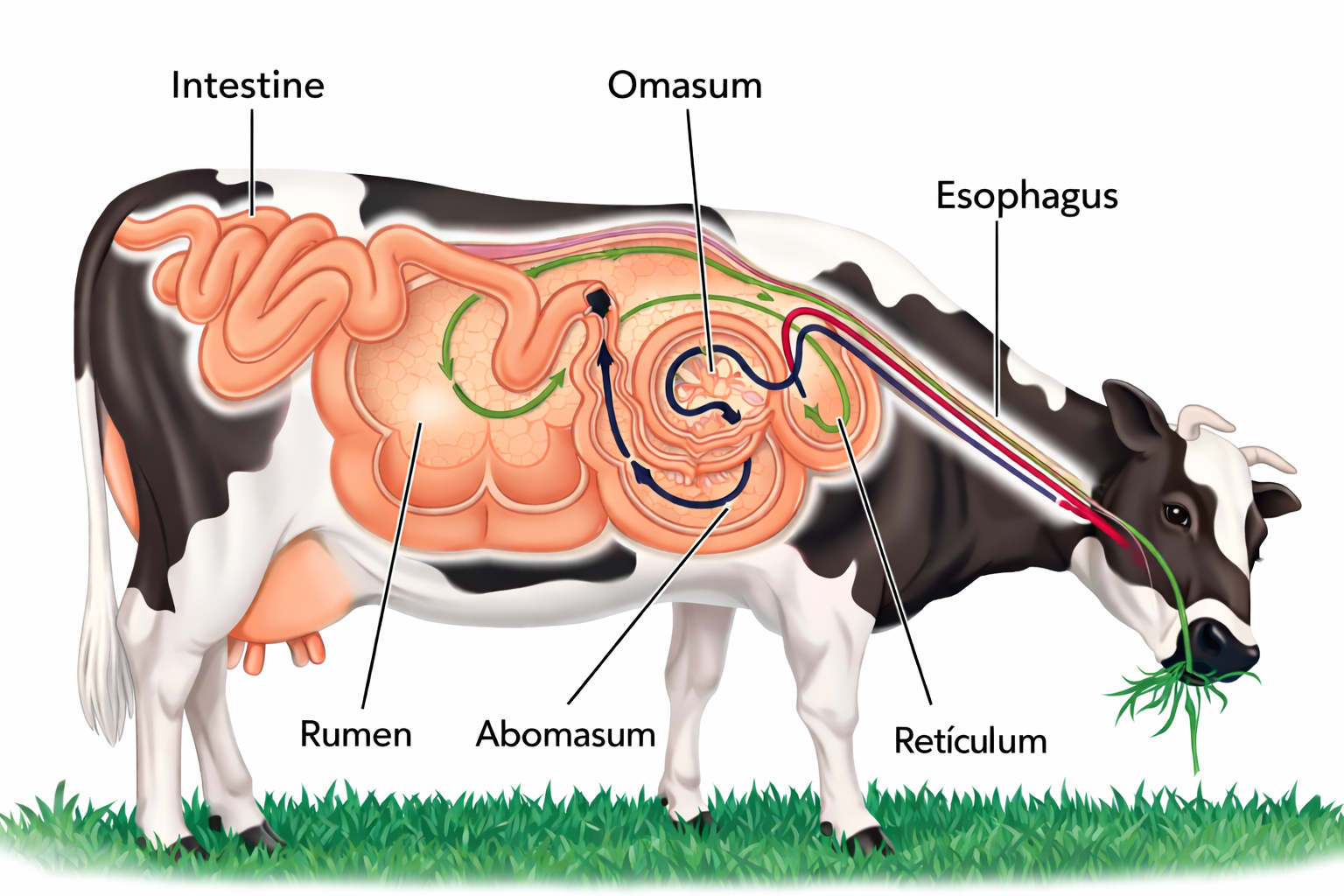
How are fats digested in ruminants?
Feed fat
Active Pathway
- Rumen → Hydrolysis of triglycerides
- Glycerol and fatty acids are released
- Microbial biohydrogenation: polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) are converted to saturated fatty acids (SFA)
- The resulting products pass to the small intestine
Inert Pathway (By-Pass)
- Protected fats pass through the rumen without significant modification
- They reach the small intestine
- Micelles are formed
- Chylomicrons and lipoproteins are formed
- They pass to the lymph
- Finally they reach the udder
Our Products
How are they obtained?
RUMINER

Calcium salts
It is a salt obtained from the union of two fatty acids and a calcium ion, after a saponification reaction.
Calcium salts of free fatty acids from palm oil (PFAD).
BENEFITS
- Higher milk production.
- Higher fat and protein.
- Improves fertility.
- Promotes total fiber digestibility.
- Reduces heat stress.
- Reduces metabolic problems associated with feeding.
- Improves immune response in lactating cows.
Nutritional values
| Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
| Fat | 84% min |
| Ash | 12% min |
| Moisture | 3% min |
| Calcium | 9% |
Fatty acid profile
| Fatty acid | Range |
|---|---|
| C16:0 | 43-52% |
| C18:0 | 3-6% |
| C18:1 | 30-40% |
| C18:2 | 5-11% |
RUMINER 60 and RUMINER 70


It is a salt obtained from the union of two fatty acids and a calcium ion, after a saponification reaction.
Calcium salts of palm fatty acids with high palmitic acid content.
BENEFITS
- Extracaloric function.
- Increase in milk fat %.
- Improves total fatty acid digestibility.
- Better feed efficiency.
- Improvements in reproduction and body condition.
- Healthier milk.
Nutritional values
| Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
| Fat | 85% min |
| Ash | 12% min |
| Moisture | 3% min |
| Calcium | 9% |
NL C16

High in palmitic acid
Fat with high palmitic acid content, obtained by physical separation of fatty acids from palm oil.
Composed of free fatty acids, with a high content of C16:0 (85-90%).
Melting point: 56-57°C
BENEFITS
- Increase in ration energy density.
- Improvement in milk production.
- Improves body condition (prevents NEB).
- Improves reproductive indices.
- Reduces metabolic problems.
- Improves animal health status.
Nutritional values
| Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
| Fat | 99% min |
| Moisture | 0.1% min |
Fatty acid profile
| Fatty acid | Range |
|---|---|
| C16:0 | 85-90% |
| C18:0 | 7-15% |
| C18:1 | 3-8% |
| C18:2 | 2% |
HIDROFAT

Hydrogenated bypass fats
Inert fats obtained from fatty acids of palm oil from physical refining, hydrogenated.
Melting point: 56-57°C
BENEFITS
- Increase in ration energy density.
- Improvement in milk production.
- Improves body condition (prevents NEB).
- Improves reproductive indices.
- Reduces metabolic problems.
- Improves animal health status.
Nutritional values
| Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
| Fat | 99% min |
| Moisture | 0.1% min |
Fatty acid profile
| Fatty acid | Range |
|---|---|
| C14:0 | <3% |
| C16:0 | 40-55% |
| C18:0 | 44-52% |
| C18:1 | 1-5% |
LIPIBIOTIC

Medium-chain fatty acids
Nutritional supplement resulting from the blend of medium-chain fatty acids (MCFA).
Fatty acid composition
| Fatty acid | Systematic name | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Caproic acid | Hexanoic acid | C6:0 |
| Caprylic acid | Octanoic acid | C8:0 |
| Capric acid | Decanoic acid | C10:0 |
| Lauric acid | Dodecanoic acid | C12:0 |
BENEFITS
- Bactericidal and bacteriostatic.
- Improves the immune system.
- Reduces the use of antibiotics.
- Prevents metabolic problems.
- Improves digestibility.
- Improves feed conversion ratio.
- Decreases somatic cell count.
- Better animal health status.
Nutritional values
| Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
| Fat | 48% min |
| Ash | 51.5% min |
| Moisture | 1.5% min |
| Calcium | 2% |
RUMINER ω 9
Calcium salts

Calcium salts of fatty acids from olive oil.
Modifies the fatty acid profile of milk fat; with healthy characteristics for human consumption.
BENEFITS
- High percentage of mostly polyunsaturated fat.
- Improves emulsification and micelle formation.
- Greater intestinal digestibility.
- Improves animal health status.
- Improves milk production and milk components.
- Improves productive indices in finishing animals.
- Improves carcass yield and quality in finishing animals.
Nutritional values
| Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
| Fat | 72.5% min |
| Ash | 11.8% |
| Moisture | 10.5% |
| Calcium | 6% min |
Fatty acid profile
| Fatty acid | Range |
|---|---|
| C16:0 | 12-20% |
| C18:0 | 3-5% |
| C18:1 | 64-70% |
| C18:2 | 9-15% |
RUMINER ω 6
Calcium salts

Calcium salts of fatty acids from a blend of vegetable oils rich in omega 6.
BENEFITS
- Energy source to cover needs at the end of gestation and the beginning of lactation.
- Increases the production of prostaglandin 2α, important at the time of calving and postpartum.
- Increases the inflammatory state of the cow.
- Increases the immunological response.
Fatty acid profile
| Fatty acid | Range |
|---|---|
| C16:0 | 10-14% |
| C18:0 | 4-6% |
| C18:1 | 28-37% |
| C18:2 | 45-55% |
RUMINER ω 3

Calcium salts
Calcium salts of fatty acids from fish oil and flax.
BENEFITS
- Energy source to cover high production needs up to peak lactation.
- Inhibits the production of prostaglandin 2α.
- Promotes PROGESTERONE production (pregnancy maintenance).
- Promotes a healthy and potent immune status.
Fatty acid profile
| Fatty acid / Group | Range |
|---|---|
| ≤C14:0 | <5% |
| EPA+DHA | 20-22% |
| OMEGA 3 | 25-30% |
| OMEGA 6 | 3-7% |